Objective To examine the associations between the number of days per week achieving various daily step thresholds and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease (CVD) incidence in older women.Methods We conducted a prospective cohort study of 13 547 women free of CVD and cancer (mean age 71.8 years). We included participants who wore an ActiGraph GT3X+ accelerometer for… Continue reading Association between frequency of meeting daily step thresholds and all-cause #mortality and #cardiovascular disease in older women
Tag: gender
#Beta-blockers after myocardial #infarction: effects according to #sex in the REBOOT trial
Background and AimsRecent trials have challenged the guideline recommendation of beta-blockers for post-myocardial infarction (MI) patients without reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Whether these recent findings apply equally to women and men remains unknown.MethodsUsing data from REBOOT (tREatment with Beta-blockers after myOcardial infarction withOut reduced ejection fracTion), the largest randomized trial evaluating the effect… Continue reading #Beta-blockers after myocardial #infarction: effects according to #sex in the REBOOT trial
Non-fermented and fermented #milk intake in relation to risk of ischemic #heart disease and to circulating cardiometabolic proteins in swedish #women and men: Two prospective longitudinal cohort studies with 100,775 participants
BackgroundThe effect of milk on the risk of ischemic heart disease (IHD) and acute myocardial infarction (MI) is unclear. We aimed to examine the association between non-fermented and fermented milk consumption on these endpoints and investigate the relationship between milk intake and cardiometabolic-related proteins in plasma.MethodsOur study is based on two Swedish prospective cohort studies… Continue reading Non-fermented and fermented #milk intake in relation to risk of ischemic #heart disease and to circulating cardiometabolic proteins in swedish #women and men: Two prospective longitudinal cohort studies with 100,775 participants
#Sex and mental #health are related to subcortical #brain microstructure
SignificanceWe demonstrate the presence of large sex-related differences in the microstructure of subcortical gray matter using advanced noninvasive diffusion MRI in a large cohort of young adults. These sex differences are found in several key brain structures that are important for mental health and are consistent with experimental studies in animals showing cellular differences in… Continue reading #Sex and mental #health are related to subcortical #brain microstructure
Association between consumption of small #fish and all-cause #mortality among Japanese: the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study
Although small fish are an important source of micronutrients, the relationship between their intake and mortality remains unclear. This study aimed to clarify the association between intake of small fish and all-cause and cause-specific mortality.Design:We used the data from a cohort study in Japan. The frequency of the intake of small fish was assessed using… Continue reading Association between consumption of small #fish and all-cause #mortality among Japanese: the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study
#Mediterranean #Diet Adherence and Risk of All-Cause #Mortality in #Women
Key PointsQuestion Is adherence to the Mediterranean diet associated with lower mortality in a US female population, and if so, what are possible biological mechanisms? Findings In this cohort study of 25 315 women followed up for 25 years, higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% reduced risk of all-cause mortality. Biomarkers of small… Continue reading #Mediterranean #Diet Adherence and Risk of All-Cause #Mortality in #Women
Sex differences in #adipose #insulin resistance are linked to #obesity, lipolysis and insulin receptor substrate 1
Background/ObjectiveInsulin resistance is more prominent in men than women. If this involves adipose tissue is unknown and was presently examined.Subjects/MethodsAdipoIR (in vivo adipose insulin resistance index) was measured in 2344 women and 787 men. In 259 of the women and 54 of the men, insulin induced inhibition of lipolysis (acylglycerol breakdown) and stimulation of lipogenesis… Continue reading Sex differences in #adipose #insulin resistance are linked to #obesity, lipolysis and insulin receptor substrate 1
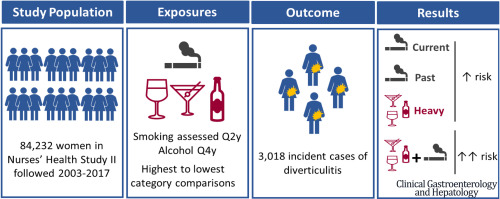
#Smoking and #Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Incident #Diverticulitis in Women
Much of what is known about the effects of alcohol and tobacco use on diverticular disease derives from studies of asymptomatic diverticulosis or complicated diverticulitis. We examined smoking and alcohol consumption and risk of incident diverticulitis in a large cohort of women.MethodsWe conducted a prospective study of 84,232 women in the Nurses’ Health Study II… Continue reading #Smoking and #Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Incident #Diverticulitis in Women
The #sex gap in #bladder cancer survival — a missing link in bladder #cancer care?
The differences in bladder cancer outcomes between the sexes has again been highlighted. Uncommon among cancers, bladder cancer outcomes are notably worse for women than for men. Furthermore, bladder cancer is three to four times more common among men than among women. Factors that might explain these sex differences include understanding the importance of haematuria… Continue reading The #sex gap in #bladder cancer survival — a missing link in bladder #cancer care?